Grams molecules and moles worksheet – Embark on an educational journey with the Grams, Molecules, and Moles Worksheet, an invaluable resource that empowers you to grasp fundamental chemistry concepts. This worksheet unravels the intricate relationship between grams, molecules, and moles, providing a solid foundation for understanding chemical reactions and quantitative analysis.
Delve into the fascinating world of chemistry as we explore Avogadro’s Number, molar mass, percent composition, empirical and molecular formulas, and chemical reactions. Prepare to unravel the mysteries of chemistry and gain a deeper appreciation for the molecular world around us.
Grams, Molecules, and Moles
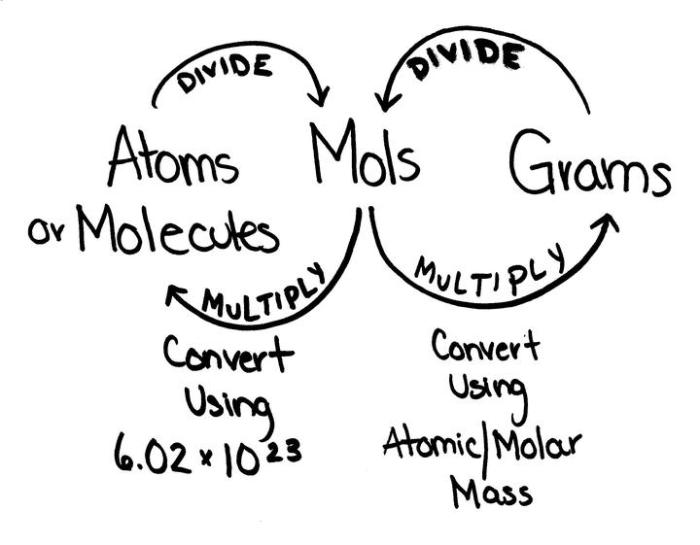
The mole is a fundamental unit in chemistry that represents a specific amount of a substance. It is defined as the amount of substance that contains as many elementary entities (atoms, molecules, ions, or electrons) as there are atoms in 0.012 kilograms of carbon-12.
The mole concept is crucial in chemistry because it provides a bridge between the macroscopic and microscopic scales. It allows us to relate the mass of a substance to the number of particles it contains, which is essential for understanding chemical reactions and other processes.
The relationship between grams, molecules, and moles can be summarized as follows:
1 mole of a substance contains Avogadro’s number (6.022 × 10 23) of particles.
The molar mass of a substance is the mass of one mole of that substance.
The number of moles of a substance can be calculated using the following formula:
Moles = Mass (g) / Molar Mass (g/mol)
Avogadro’s Number, Grams molecules and moles worksheet
Avogadro’s number is the number of particles (atoms, molecules, ions, or electrons) contained in one mole of a substance. It is equal to 6.022 × 10 23.
Avogadro’s number is a fundamental constant in chemistry. It allows us to convert between the mass and the number of particles in a substance.
For example, if we know the molar mass of a substance, we can use Avogadro’s number to calculate the number of particles in a given mass of that substance.
Molar Mass
The molar mass of a substance is the mass of one mole of that substance.
The molar mass of an element is the atomic mass of that element.
The molar mass of a compound is the sum of the atomic masses of the elements that make up the compound.
The molar mass of a substance can be used to calculate the number of moles of that substance in a given mass.
For example, if we know the mass and the molar mass of a substance, we can use the following formula to calculate the number of moles of that substance:
Moles = Mass (g) / Molar Mass (g/mol)
Percent Composition
Percent composition is the percentage by mass of each element in a compound.
The percent composition of a compound can be used to determine the empirical formula of the compound.
The empirical formula of a compound is the simplest whole-number ratio of the elements in the compound.
The molecular formula of a compound is the actual number of atoms of each element in the compound.
The molecular formula of a compound can be determined from the empirical formula and the molar mass of the compound.
Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions are processes in which substances are transformed into new substances.
Chemical reactions can be represented by chemical equations.
Chemical equations show the reactants and products of a reaction, as well as the stoichiometry of the reaction.
Stoichiometry is the study of the quantitative relationships between the reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
Stoichiometry can be used to calculate the amounts of reactants and products that are needed or produced in a chemical reaction.
Key Questions Answered: Grams Molecules And Moles Worksheet
What is the significance of Avogadro’s Number?
Avogadro’s Number represents the number of atoms, molecules, or ions present in one mole of a substance, providing a fundamental conversion factor between mass and quantity.
How do I calculate the molar mass of a compound?
To calculate the molar mass, add the atomic masses of all atoms in the compound’s molecular formula, using the periodic table as a reference.
What is the difference between empirical and molecular formulas?
An empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of elements in a compound, while a molecular formula indicates the exact number of each type of atom present in a molecule.