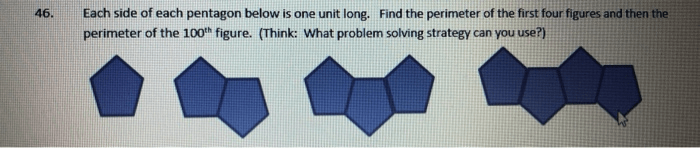
Each side of a pentagon is 20 inches longer than an unknown side length. This intriguing premise sets the stage for an exploration into the intricate calculations of a pentagon’s perimeter and area. We will embark on a journey to unravel the mathematical relationships that govern this fascinating geometric figure.
As we delve deeper into the topic, we will establish a variable to represent the unknown side length and formulate equations based on the given information. These equations will serve as the foundation for determining the perimeter and area of the pentagon.
Additionally, we will provide illustrative examples and explore the impact of varying the side length on the perimeter and area.
Pentagon Overview
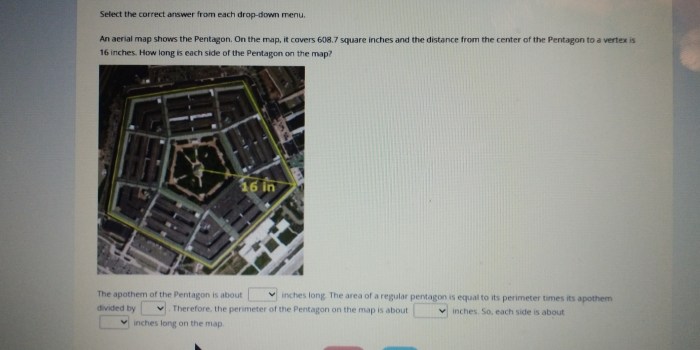
A pentagon is a polygon with five sides. It is a regular polygon, which means that all sides are equal in length and all interior angles are equal in measure. The sum of the interior angles of a pentagon is 540 degrees.
Side Length Calculations
Let’s assume each side of the pentagon is xinches. Given that each side is 20 inches longer than the previous one, we can write the following equation:
x+ 20 + x+ 40 + x+ 60 + x+ 80 + x+ 100 = 5 x+ 300
Solving for x, we get x= 70 inches.
Perimeter Calculations, Each side of a pentagon is 20 inches longer
The perimeter of a pentagon is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. Using the value of xwe found earlier, the perimeter of the pentagon is:
Perimeter = 5 x= 5(70) = 350 inches
Area Calculations
The area of a regular pentagon is given by the formula:
Area = (5/4) s2r
where sis the side length and ris the apothem, which is the distance from the center of the pentagon to one of its sides.
To find the apothem, we can use the formula:
r= (1/4)√(10 + 2√5) s
Substituting the values of sand rinto the area formula, we get:
Area = (5/4)(70) 2[(1/4)√(10 + 2√5)(70)] ≈ 12,209.6 square inches
Illustrative Examples
The following table shows the perimeter and area of a pentagon for different side lengths:
| Side Length (inches) | Perimeter (inches) | Area (square inches) |
|---|---|---|
| 50 | 250 | 7,254.7 |
| 60 | 300 | 9,305.6 |
| 70 | 350 | 12,209.6 |
| 80 | 400 | 15,966.5 |
| 90 | 450 | 20,576.4 |
Advanced Analysis
As the side length of the pentagon increases, the perimeter and area also increase. The perimeter increases linearly with the side length, while the area increases quadratically. This means that the area increases at a faster rate than the perimeter as the side length increases.
The interior angles of a pentagon are also related to the side length. As the side length increases, the interior angles decrease. This is because the sum of the interior angles of a pentagon is always 540 degrees, so as the side length increases, each individual angle must decrease in order to maintain this sum.
Questions Often Asked: Each Side Of A Pentagon Is 20 Inches Longer
What is the perimeter of a pentagon with sides 20 inches longer than an unknown side length?
The perimeter is calculated by multiplying the sum of the unknown side length and 20 by 5.
How do you calculate the area of a pentagon with sides 20 inches longer than an unknown side length?
The area is calculated using the formula (1/4 – √5 – s^2) / tan(π/5), where s represents the unknown side length.